HOW TO DESIGN POWER CONVERTERS WITH IGBTS
 We all remember those famous words uttered by the brave Jedi, Luke Skywalker, “But I was going into Tosche Station to pick up some power converters!”
We all remember those famous words uttered by the brave Jedi, Luke Skywalker, “But I was going into Tosche Station to pick up some power converters!”
Apparently, power converters have universal applications. Whether you’re running a moisture farm on Tatooine or designing a vehicle that operates here on Earth, you’re going to need power converters.
These devices transform electrical power from one form to another, depending on the needs of the equipment you want to use. One important example is an inverter, which employs semiconductor switches called insulated gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs) to convert direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC).
IGBTs are suitable for power conversion applications because they operate at high voltages and currents. Additionally, heat generation decreases IGBT reliability. As a result, these switches must be designed properly to minimize thermal issues.
General purpose printed circuit boards (PCBs) also suffer from thermal and reliability issues. To learn more, watch the webinar Ansys Icepak and Ansys Sherlock for Thermal Cycling.
Simulation Workflow to Design Power Converters
Inverters play a dominant role in many applications for powering AC loads in our homes, cars, offices, buildings and high-power transportation systems such as electric trains. In variable frequency drives, the inverters are used to regulate the speed and torque of AC motors.
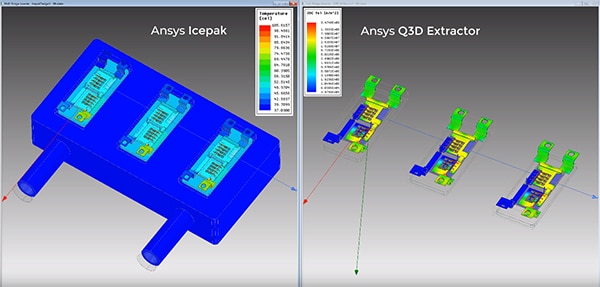
You can design these IGBTs using Ansys Q3D Extractor and Ansys Icepak. These simulation tools help engineers optimize the reliability and performance of these power systems.
Q3D Extractor and Icepak can be used to predict the electrothermal effects and safe operating temperatures for power converters, providing critical reliability and stability insights.
For example, power losses from an IGBT design are analyzed in Q3D Extractor and then transferred into Icepak to perform a coupled electrothermal simulation. The simulation predicts safe operating temperatures of these devices and improves their stability and reliability.
“As the world moves toward more electrified modes of transportation, electrothermal simulation becomes an essential tool for designers to create vehicle systems that will work reliably under the stresses of real-life operating conditions,” says Eric Bracken, chief technologist at Ansys.
Thermal effects in power inverters can also lead to deformation and stress in their electrical connections. Metal fatigue and creep become more pronounced at higher temperatures. Thermal simulation results are also used as inputs to study the structural reliability of the converter.
To learn about our automated process of thermal modeling of printed circuit boards, watch the webinar Ansys Icepak and Ansys Sherlock for Thermal Cycling.
Any and all ANSYS, Inc. brand, product, service and feature names, logos and slogans such as Ansys, Ansys Icepak, Ansys Sherlock and Ansys Q3D Extractor are registered trademarks or trademarks of ANSYS, Inc. or its subsidiaries in the United States or other countries.
An Ansys Q3D Extractor simulation of the magnetic field on a half-bridge inverter that utilizes IGBTs.