Ansys Fluent Aero 2025 R1 Updates – Aerospace and Defense
Fluent Aero – Mesh Adaption (Beta) and Parametric Search (Beta)
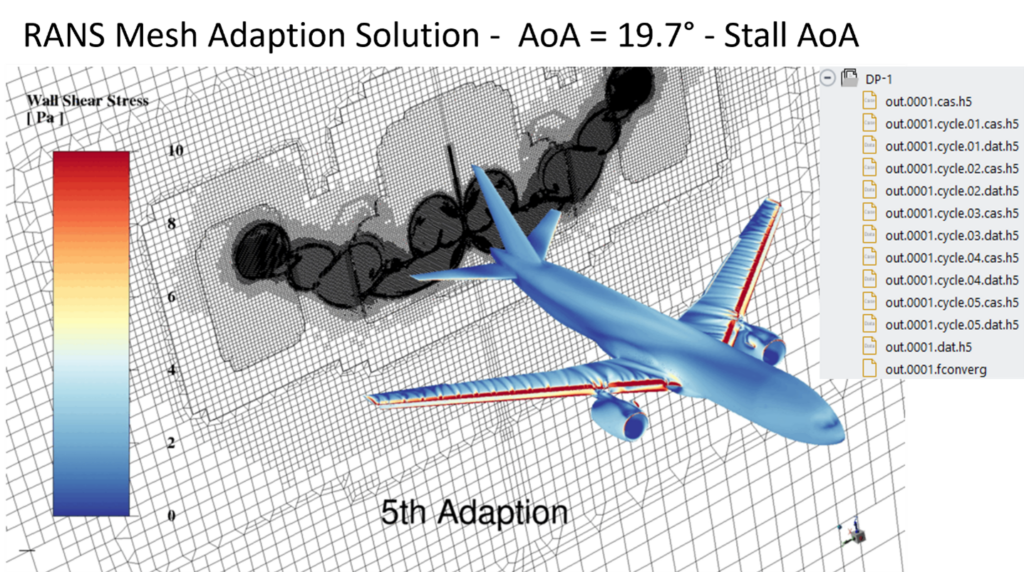
This feature automatically adapts the baseline mesh of the simulation using the polyhedral unstructured mesh adaption (PUMA) in combination with the Combined Hessian Indicator. Mesh adaption cycles are used to progressively refine the baseline mesh in order to reveal the most salient flow features, shocks, wakes, etc. of your simulation, therefore improving the precision of CFD calculations. This feature helps users to achieve accurate mesh independent solutions that capture detailed flow phenomena that may not have been possible using a baseline mesh over a wide range of conditions.
Numerous Features for Turbulence Modeling added to GPU solver
– Generic WMLES model, which uses LES for the bulk of the domain and the algebraic RANS model for the thin near-wall section of the boundary layer
– Algebraic Transition and Curvature Correction models are now available for the k-omega SST and GEKO models
– Wall Roughness for Epsilon-Based Models
– Optimized LES Numerics
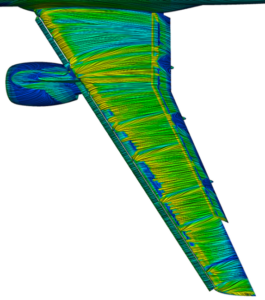
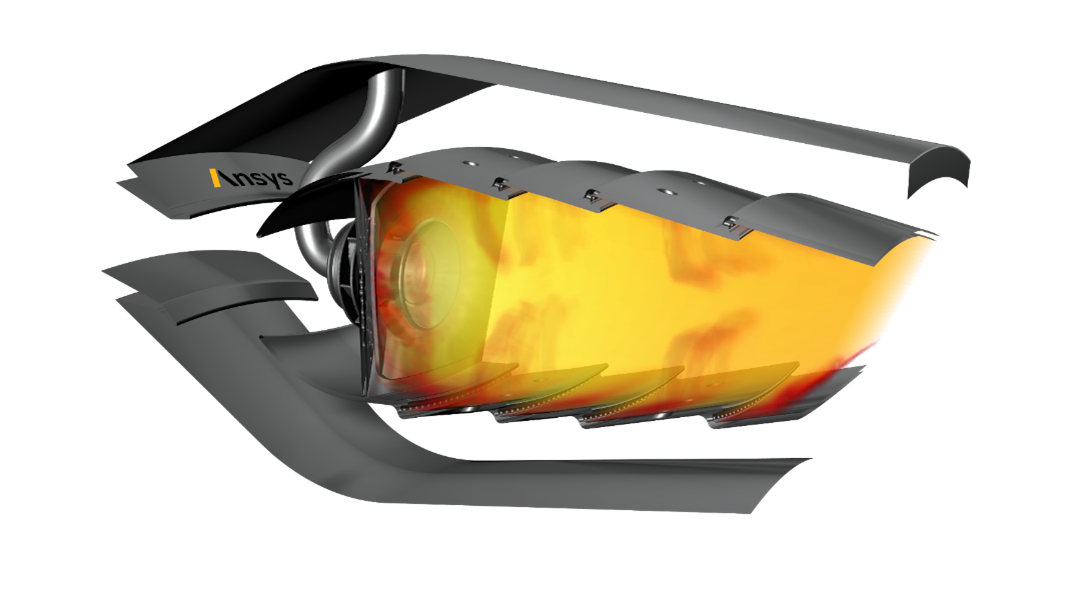
Rapid Octree + GPU solver LES analysis of an Aircraft
The Rapid Octree mesher is based on massively parallel algorithms and data structures. It allows you to use an existing boundary geometry to generate a new volume mesh that is based on cube cells, such that the resulting meshes are mostly isotropic. This type of mesh is particularly appropriate for Scale Resolving Simulations (LES).
One billion cells were generated using the Rapid Octree method in less than half an hour on 512 cores. Using a Multi-GPU of 32 L40 GPU cards, results were obtained in a day. A significant accomplishment in terms of speed-up and obtaining results in a short time period
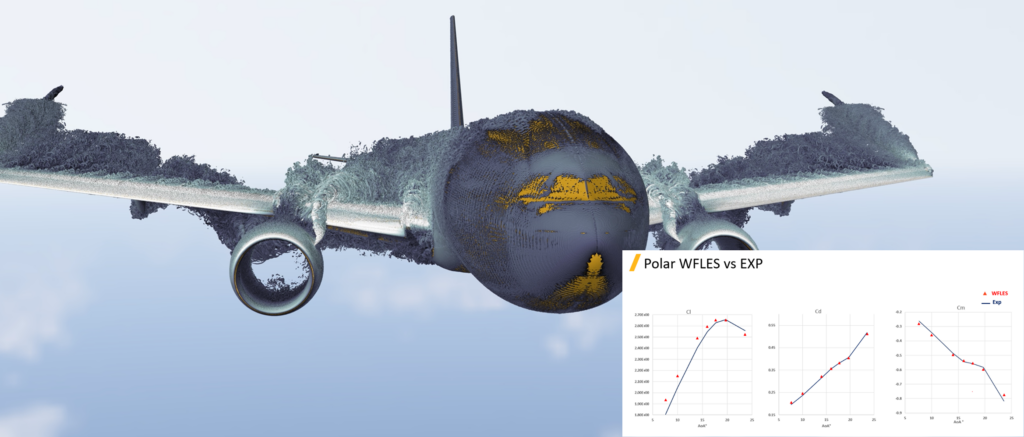
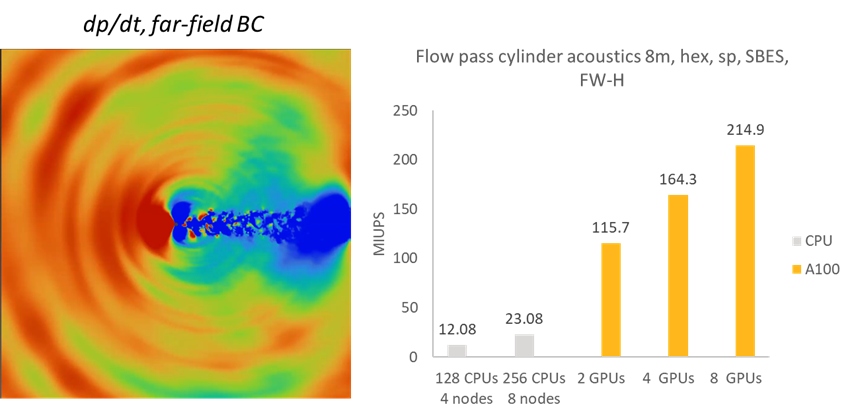
Acoustics with Ffowcs Williams & Hawkings
– Hybrid GPU (resolves flow) / CPU (resolves sound signal) solution
– Workflow is similar to the currently existing that is using the CPU solver